Causes of keratoconus
Today there are various hypotheses about why keratoconus occurs, but the exact causes and trigger mechanism of this disease are still not fully established.
Endocrine theory was one of the first. According to it, the appearance of keratoconus was associated with a violation of the functions of the endocrine glands, which is accompanied by a disorder of the pituitary-diencephalic system, Hypo – or hyperthyroidism, a decrease in 17-ketosteroids, adipose-genius deficiency. It is also important that the greatest progression of keratoconus is noted during the puberty period, during the growth of the body due to the activation of the endocrine glands.
A viral theory was also proposed. It appeared due to the fact that patients diagnosed with keratoconus were sick hepatitis B in 80% of cases.
There is an metabolic theory. During studies in the fluid of the anterior chamber of the eye in patients with keratoconus was revealed reduced activity of glutathione reductase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. As a result of these enzymatic disorders increases the level of lipid peroxidation, which causes the activation of the release of lysosomal hydrolytic enzymes, which lead to lysis of structures within cells.
Allergic theory. According to it, keratoconus occurs against the background of diseases of allergic etiology: asthma, allergic blepharoconjunctivitis, eczema, hay fever. The mechanism of pathology is presumably caused by a violation of immune homeostasis due to an increase in IG M, C3, C4 components of the compliment. It was found that with the progression of keratoconus, the defectiveness of T-suppressors increases and IG increases, which causes a breakdown of auto-tolerance to the antigens of the cornea. In conjunctival biopsies with keratoconus, characteristic signs of immune inflammation are revealed: high infiltration by monocytes, macrophages, lymphocytes, plasma cells and high concentration of mast cells.
The appearance of keratoconus is also associated with mechanical trauma. This occurs in the case of permanent damage to the epithelial layer due to prolonged wear of contact lenses, as well as combing the eyelids, often with allergic reactions. This constant trauma causes the start of pathological processes: chronic apoptosis of keratocytes, the enhancement of lysosomal enzymes, and inhibitors of proteases – degradation of collagen, and in the future – the development in the epithelium of the cornea degenerative processes.
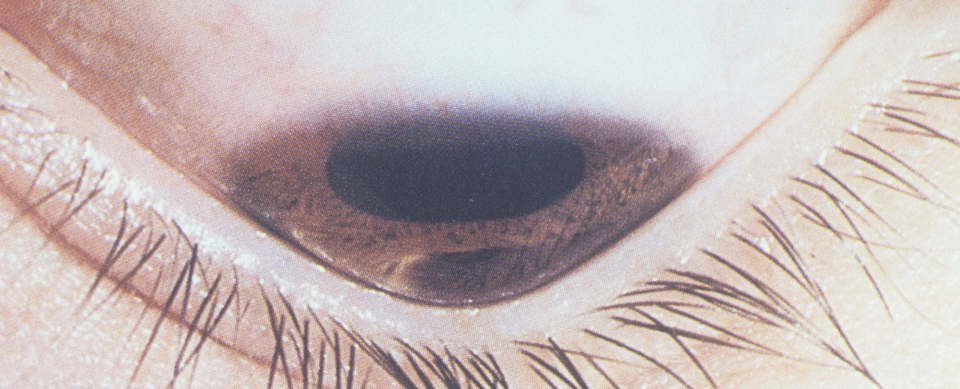
Secondary keratoconus can develop as a result of inflammatory diseases of the cornea, injuries, burns and postoperative complications leading to ectasia.
However, the most common is hereditary or genetic theory. Frequent combination of keratoconus with genetic abnormalities and hereditary syndromes: retinal pigment degeneration, Leber amaurosis, Crouzon syndrome, granular corneal dystrophy, down syndrome, Marfan syndrome and blue scler syndrome was noted. It should be noted that 68% of patients diagnosed with keratoconus have one or another pathology of connective tissue. In addition, keratoconus may be associated with mental illness, such as schizophrenia.
The autosomal-dominant type by which the keratoconus is inherited by members of the same family is described. Transmission takes place on the male line. Research conducted in USA, identified the locus of the genes that are responsible for the appearance of keratoconus. Scientists believe that this gene is COL6A1 with DNA, which encodes the production of collagen type IV. Currently, the course of research continues.
Learn more about keratoconus gene VSX1 >>>
The pathogenesis of keratoconus
The launch of keratocyte apoptosis leads to a violation of the structure of collagen fibers. Due to the fact that the location and order of stromal plates are violated, the density of endothelial cells decreases, there is a "vacuum" of the stroma and begins the loss of one of the most important functions of the cornea – sphericity. Cell structures are in a mess, their shape is changing. Perhaps the formation of turbidity in the Bowman membrane in the early stages of the disease.
In the later stages when the corneal stroma is stretched, there are located parallel to the line Vogt. Later in the area of the top of keratoconus is observed the formation of thinning and scarring. Severe forms of this pathology can be accompanied by the appearance of breaks and cracks. Characteristic only for keratoconus (pathognomonic) symptom is the formation of the ring of Fleischner-pigment subepithelial ring of green or brown-yellow color. Due to the deposition of hemosiderin, its individual arcs may appear around the top of the keratoconus. In 7% of patients there is a manifestation of various epitheliopathies. In the later stages of the disease, a conically altered cornea when viewed downwards causes a protrusion of the upper eyelid and a Y-shaped notch on the lower eyelid conjunctiva – these phenomena are called The Manson symptom.

Damage to the descemet membrane leads to the impregnation of the cornea with moisture from the anterior chamber of the eye, hydration of the cornea, which clinically appears as a spot of milky white color. There is an increase in scarring of the cornea. This is accompanied by pain and a sharp deterioration of vision. The recovery of transparency can occur for 6-8 weeks.
The terminal stage of keratoconus threatens with a possible partial rupture of the cornea. When this is observed the formation on the surface of the fluid-filled bull. In the future, there is a high risk of complete rupture of the cornea and loss of the eye, so an emergency operation for the transplantation of the donor cornea is necessary.



