The first symptoms of developing keratoconus include the need for frequent change of glasses or contact lenses, because vision problems can not be corrected with their help.
What does the patient see?
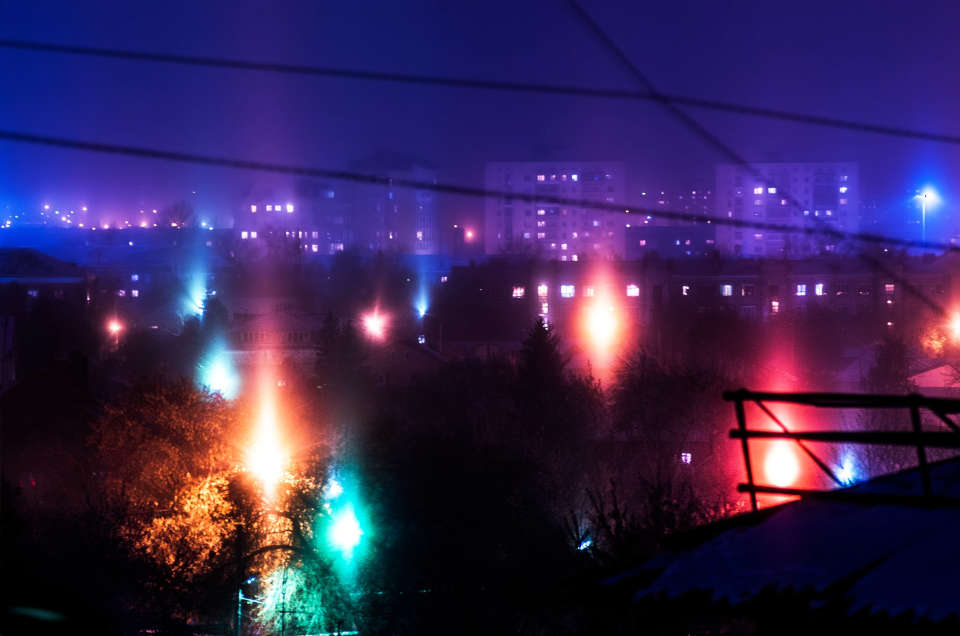
A characteristic feature of the disease is monocular polyopia - the appearance of many different imaginary images. This effect is most clearly manifested when considering high-contrast images, for example, a light point on a dark background. The patient with keratoconus in this case sees not a single point, but a chaotic cluster of many of its images.
When the patient whith keratoconus is examined by a doctor or an optometrist (for example, for the prescripttion of glasses or contact lenses), an increase in the curvature of the cornea is noted.
At night, the patient with the disease may have "halo" effects-rays around the light sources.

What should alert the doctor?
The diagnosis can also be suspected in optic by an optometrist, when when applying for the selection of glasses or contact lenses when measuring the curvature of the cornea (on a Keratometer-Refractometer) determine the increase in values. Аccording to the curvature parameter of the cornea, the following degrees of keratoconus are distinguished:
- light - less than 45 DPT;
- average – 45 to 52 Diopters;
- developed - 52-62 DPTR;
- heavy - more than 62 DPTR.
Morphologically keratoconus klassificeret for differences in the form:
- mastoid keratoconus-usually small (up to 5 mm), localized closer to the center of the cornea;
- oval keratoconus - has a size of 5-6 mm, usually located down from the center;
- spherical keratoconus is larger than 6 mm, the pathological process covers more than 75% of the cornea.
At the advanced stage of keratoconus, the disease can flow into the corneal dropsy, which is otherwise called "acute keratoconus". In this case, the liquid penetrates into the stroma through the gaps in the descemet membrane. This causes swelling, possibly secondary severe scarring of the cornea.
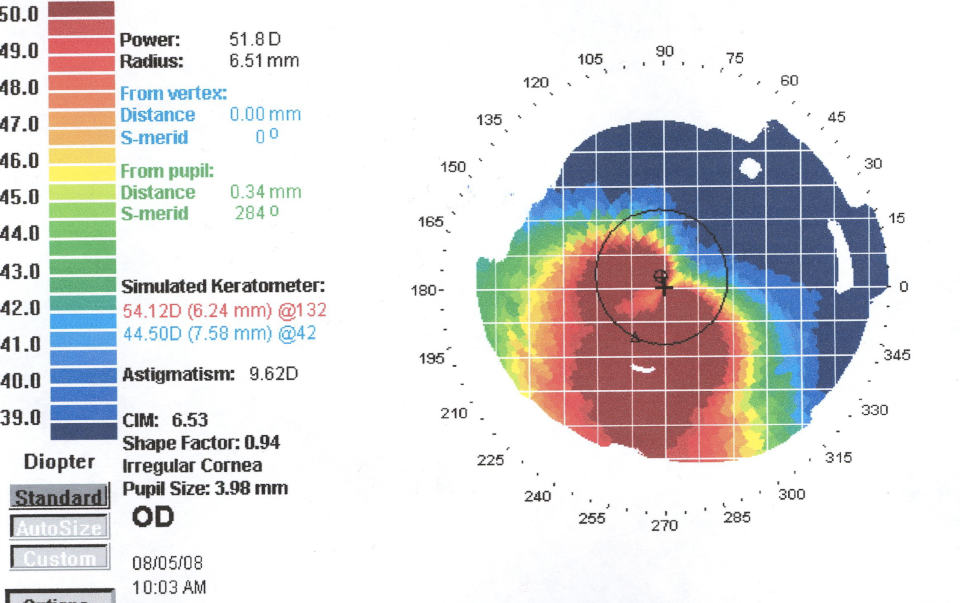
The improvement of instruments for topographic mapping (Sirius, Pentacam) and study of the cornea has greatly facilitated diagnosis of keratoconus by ophthalmologists and the choice of the best treatment option. Since in the early stages of the disease the visual function does not suffer too much, it is difficult to identify the initial keratoconus. A characteristic feature that causes suspicion in a specialist, are complications in achieving maximum visual acuity, even with the ideal selection of points.
The diagonosis of keratoconus helps to confirm the appearance of other signs of the disease: thinning of the corneal stroma, the Fleischner ring (in the basal layer of the epithelium, iron oxide deposits are found), as well as ruptures in the Bowman membrane. All these clinical manifestations of the disease are detected during the examination with a slit lamp.
Pachymetry (ultrasound, etc.) is also informative for diagnosis, it is used to determine the degree of thinning of the cornea in patients with suspected keratoconus. Modern devices, as a rule, combine the capabilities of various methods of the above studies and allow you to accurately diagnose the disease.